Prototyping laboratories
Advanced electrical and mechanical engineering design and fabrication
Our state-of-the-art prototyping capabilities enable the design, fabrication and optimization of novel devices and technologies.
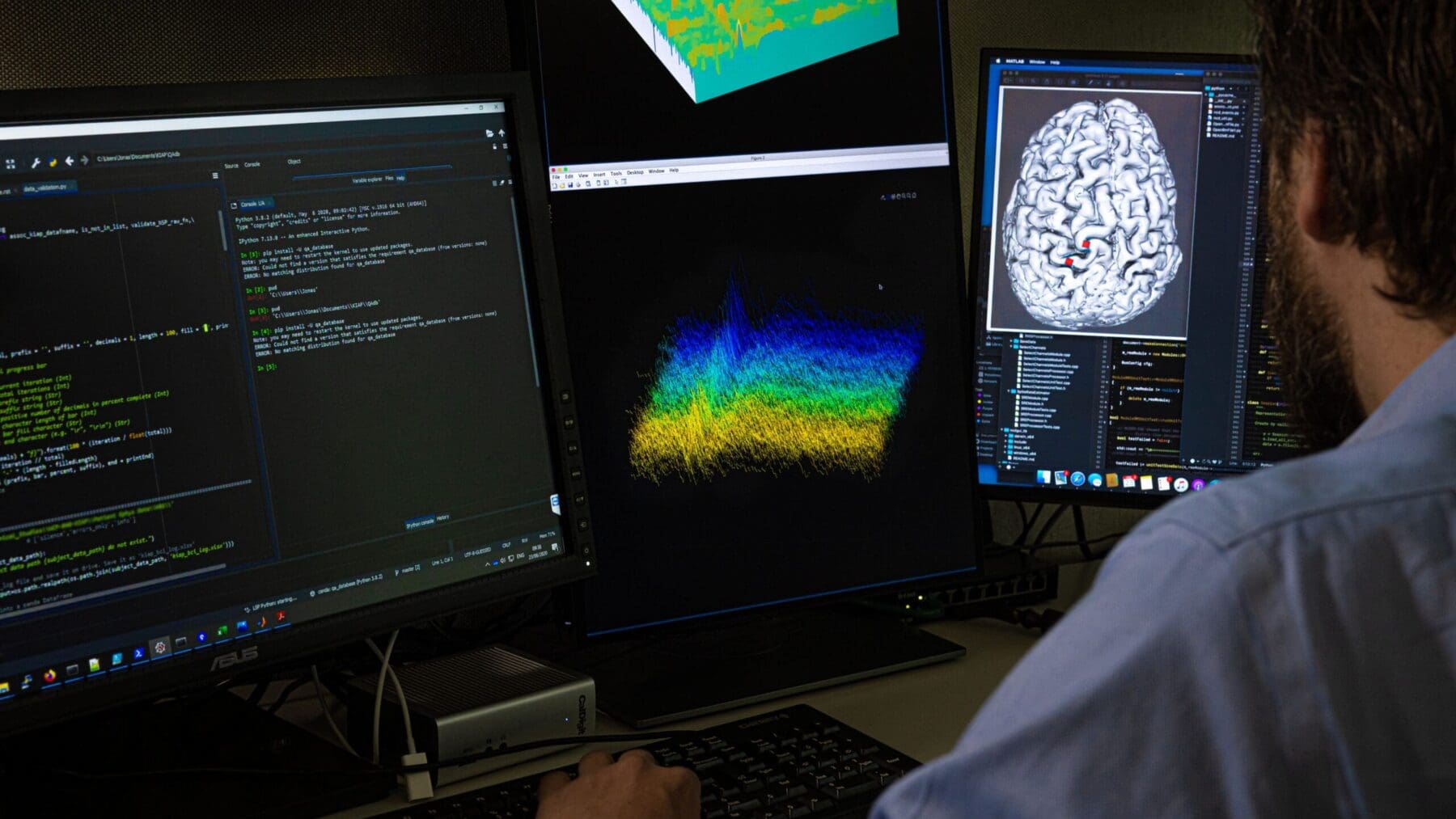
Our engineers quickly fabricate scale models of our technologies using 3D computer aided design. This allows early testing and evaluation of concepts, assessment of feasibility and translation readiness levels, rapid feedback and iterations to accelerate product development.
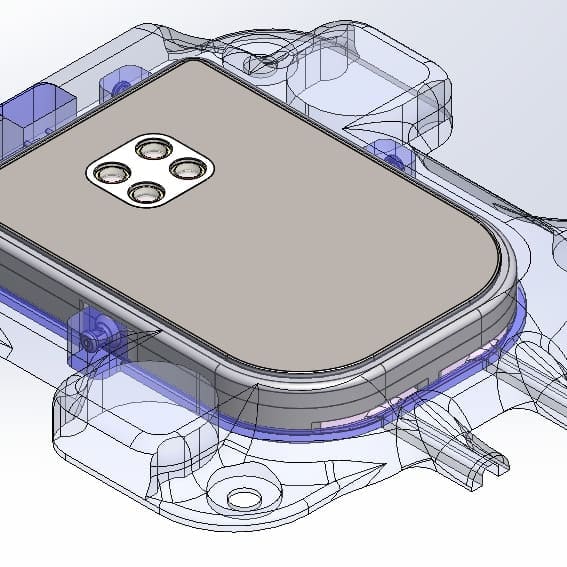
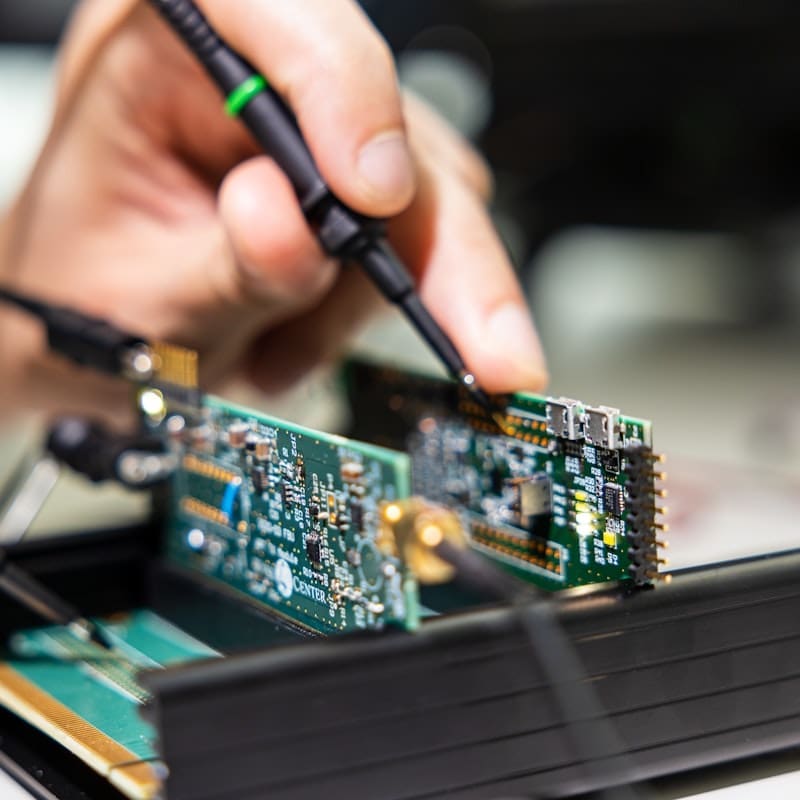
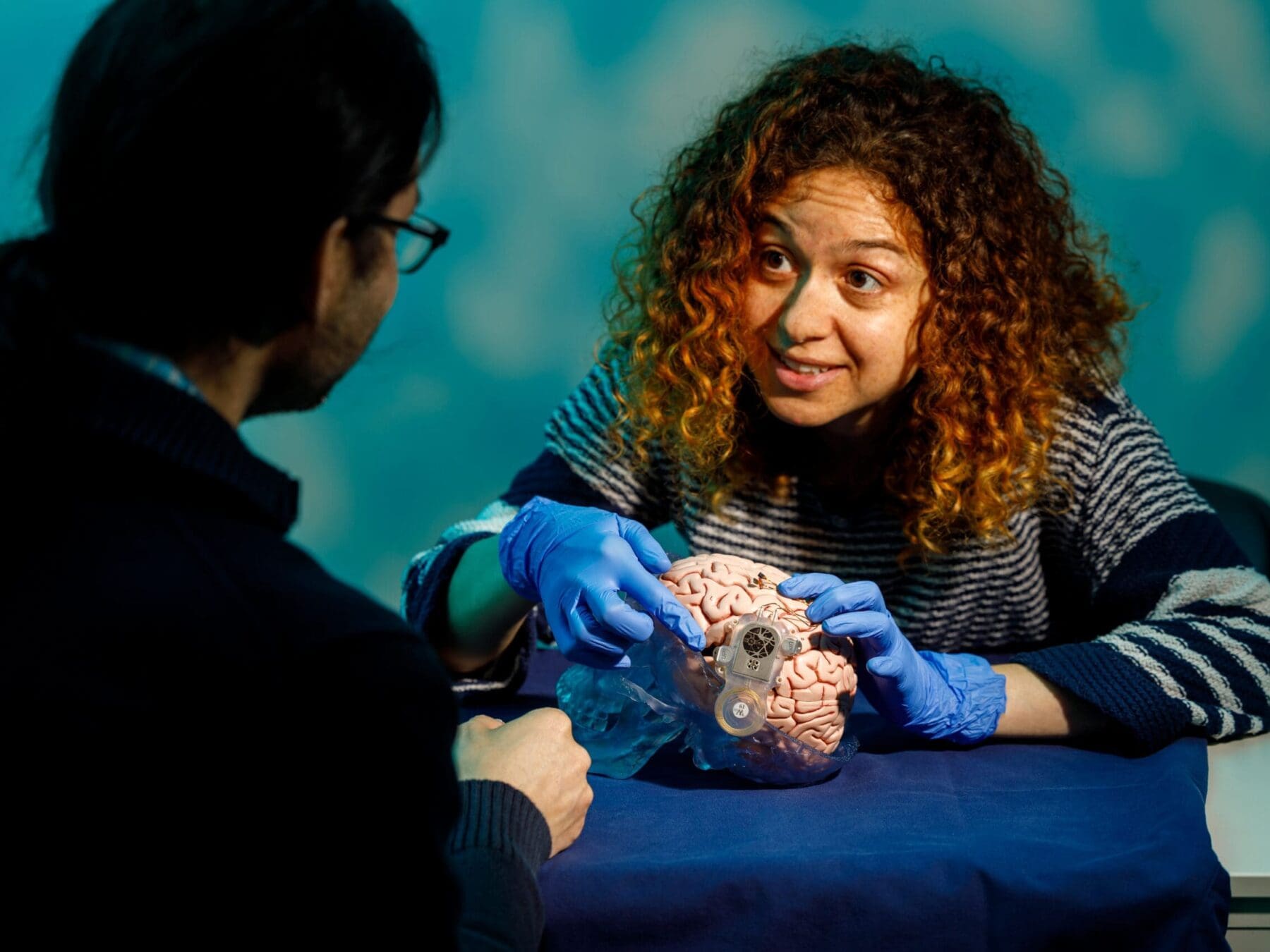
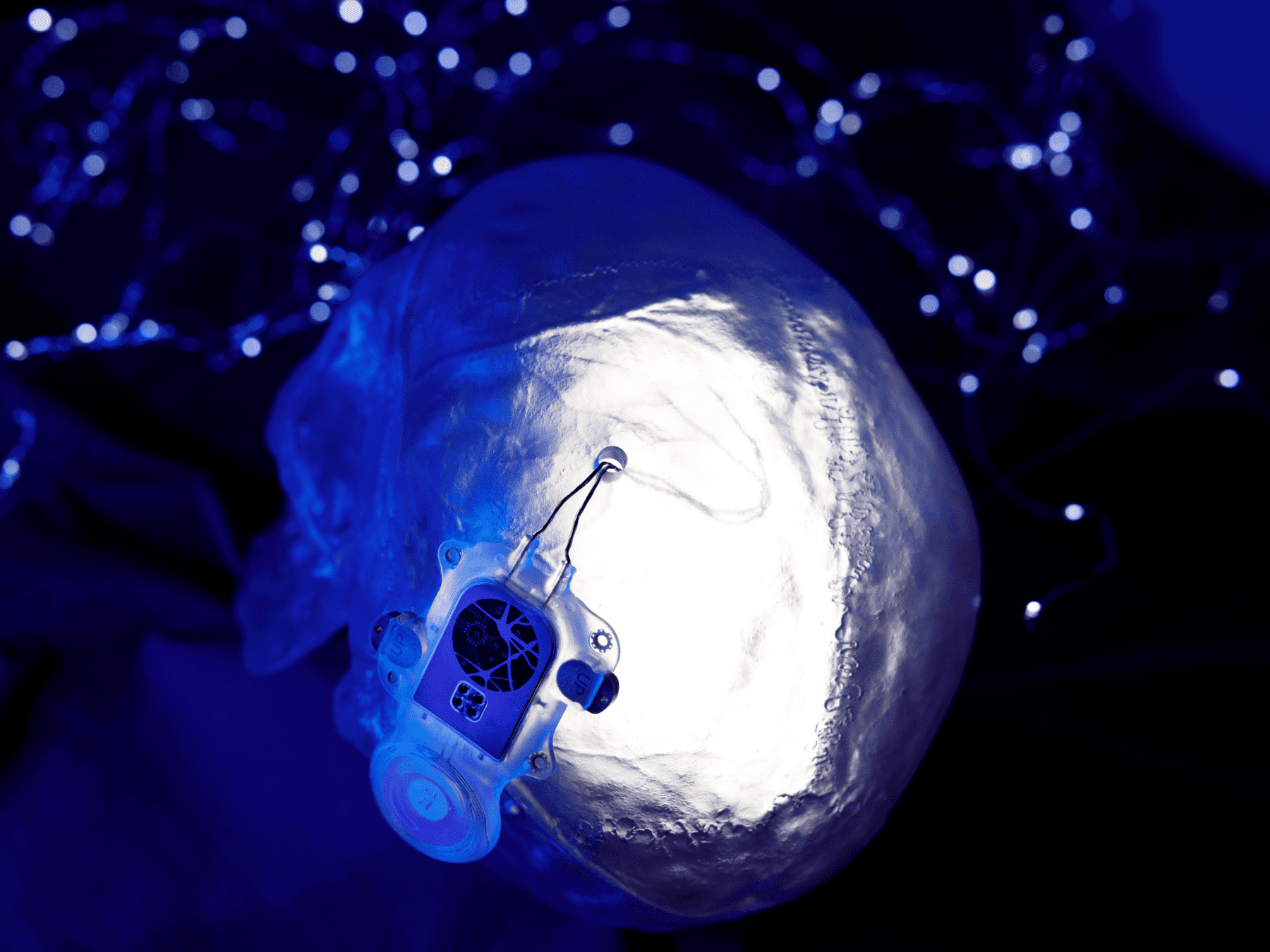
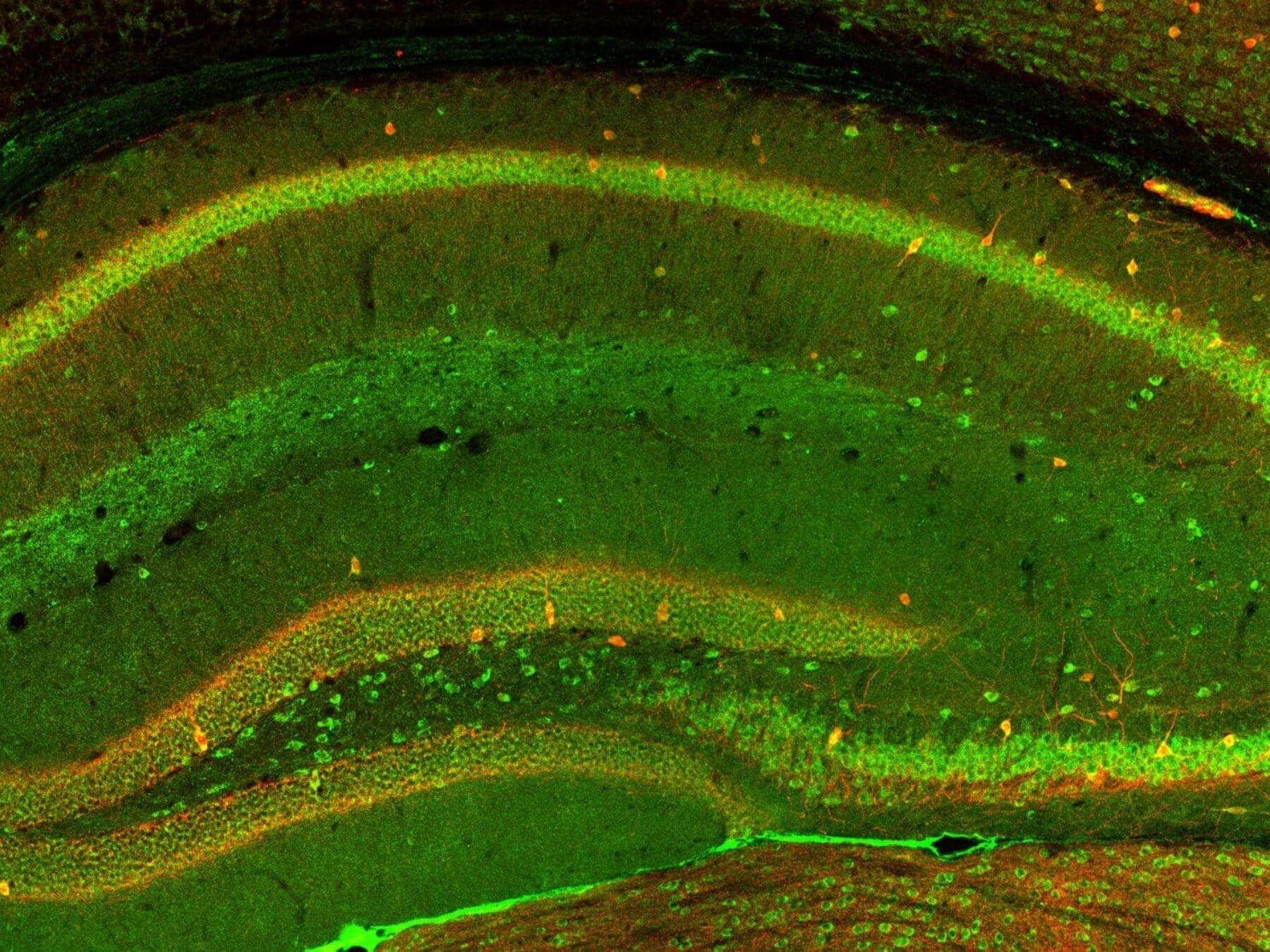
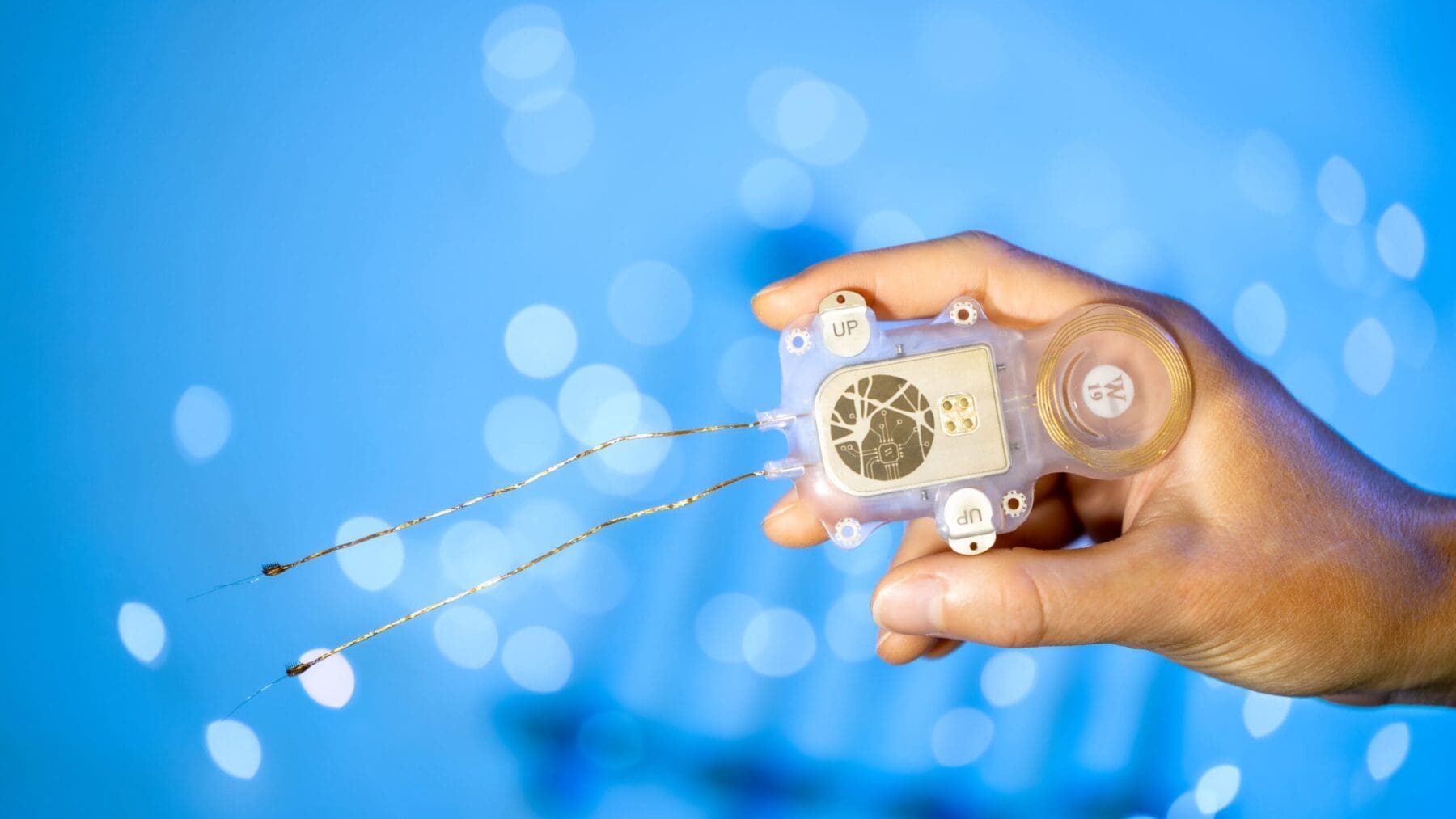
Many of the technologies we develop require the creation of micro-scale components. Microfabrication is needed for miniaturized medical implants or for components that interface directly with cells for research applications. These include sensors to measure neural activity, probes to modulate neural systems and components to support advanced cell imaging. Early integration of medical certification is included in the design and prototype development process. Our laboratories include computer-aided design and simulation, as well as workshops for fabrication, system integration and testing.
The Wyss Center's capabilities in this area include:
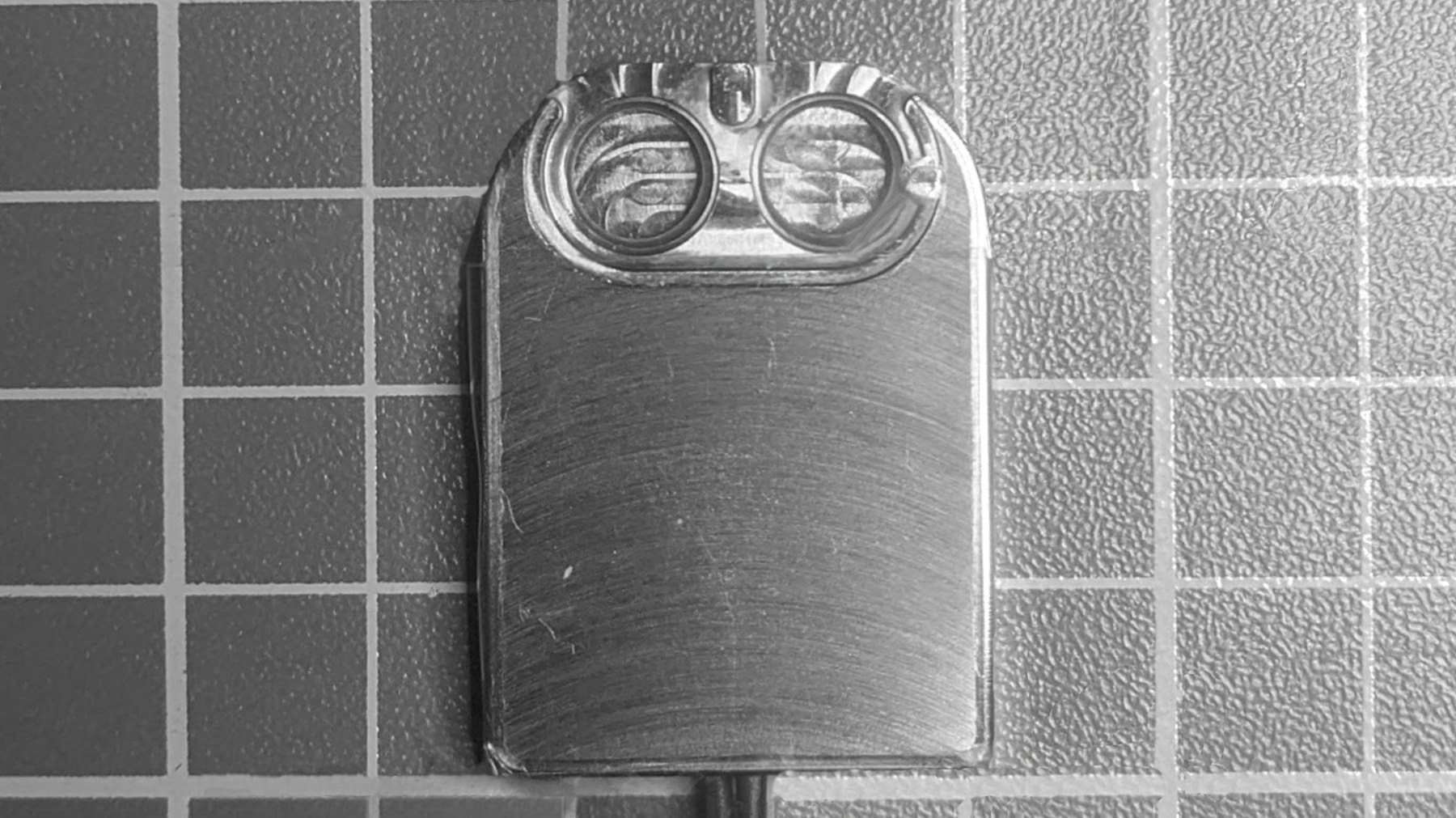

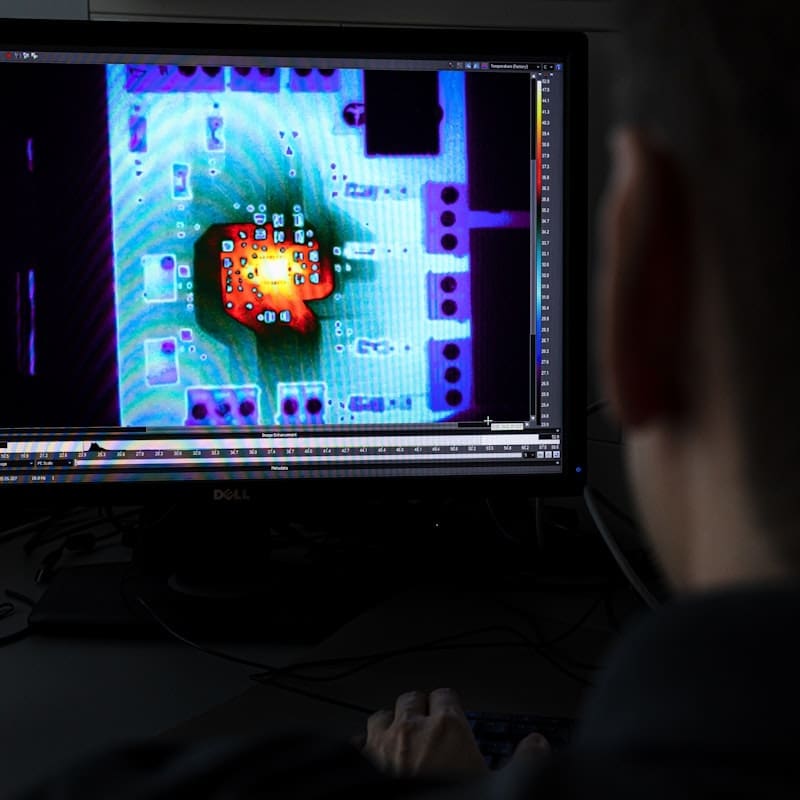
Our custom-built accelerated ageing system simulates the long-term aging of devices in the human body and helps us understand what will happen when they are implanted for long periods of time.
Accelerated aging tests are particularly useful for assessing novel encapsulation technologies. One of the major challenges of developing implantable devices is protecting the delicate internal electronics from the warm, wet and salty environment of the human body. Hermetic encapsulation of the device housing is necessary to ensure devices are leak-proof and can survive in the body for years. We evaluate hermetic and near-hermetic encapsulation solutions and integrate them into implantable medical devices then test their capacity to withstand moisture and mechanical damage.
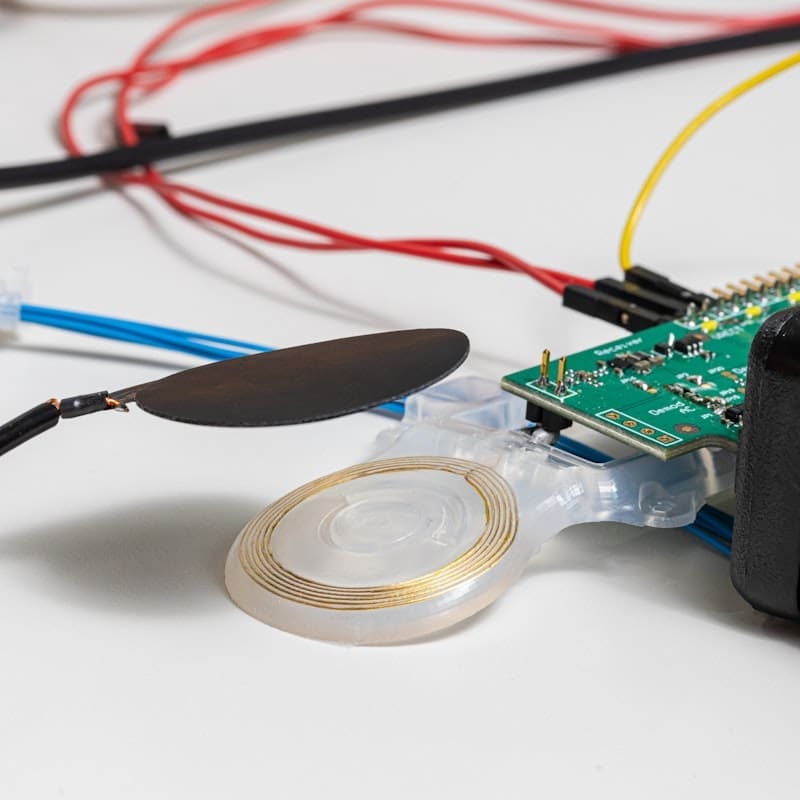
Our system subjects the prototype device to an environment in which high temperatures and humidity accelerates aging. An electronic tag built into the device wirelessly sends updates on temperature and performance. This process gives valuable information on the ageing of electronics and the encapsulation performance.
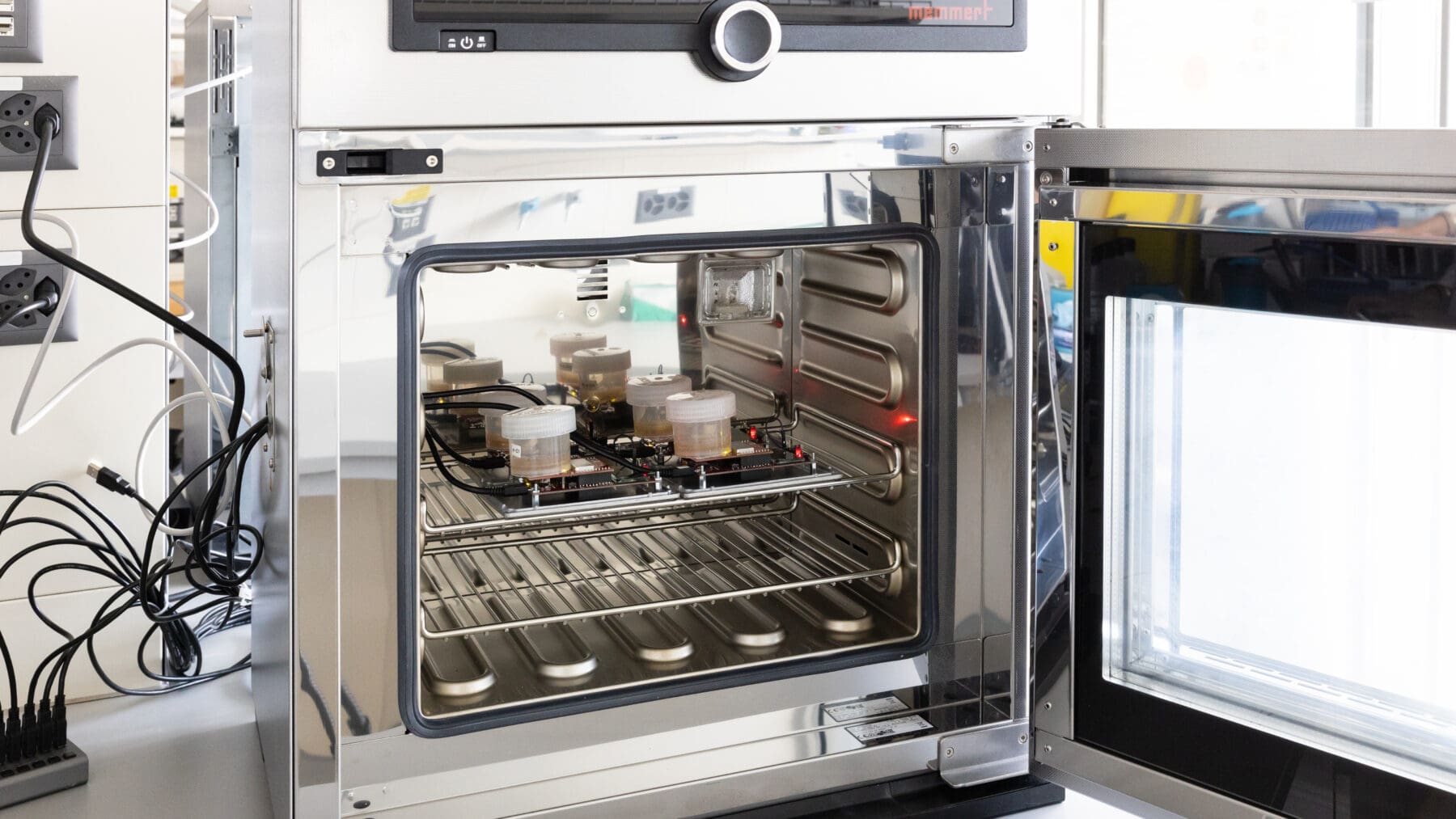

Our custom-built accelerated ageing system.