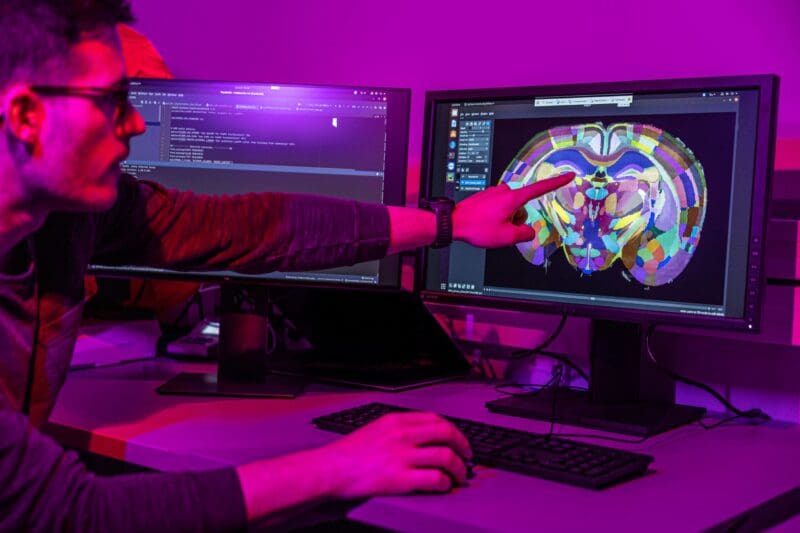
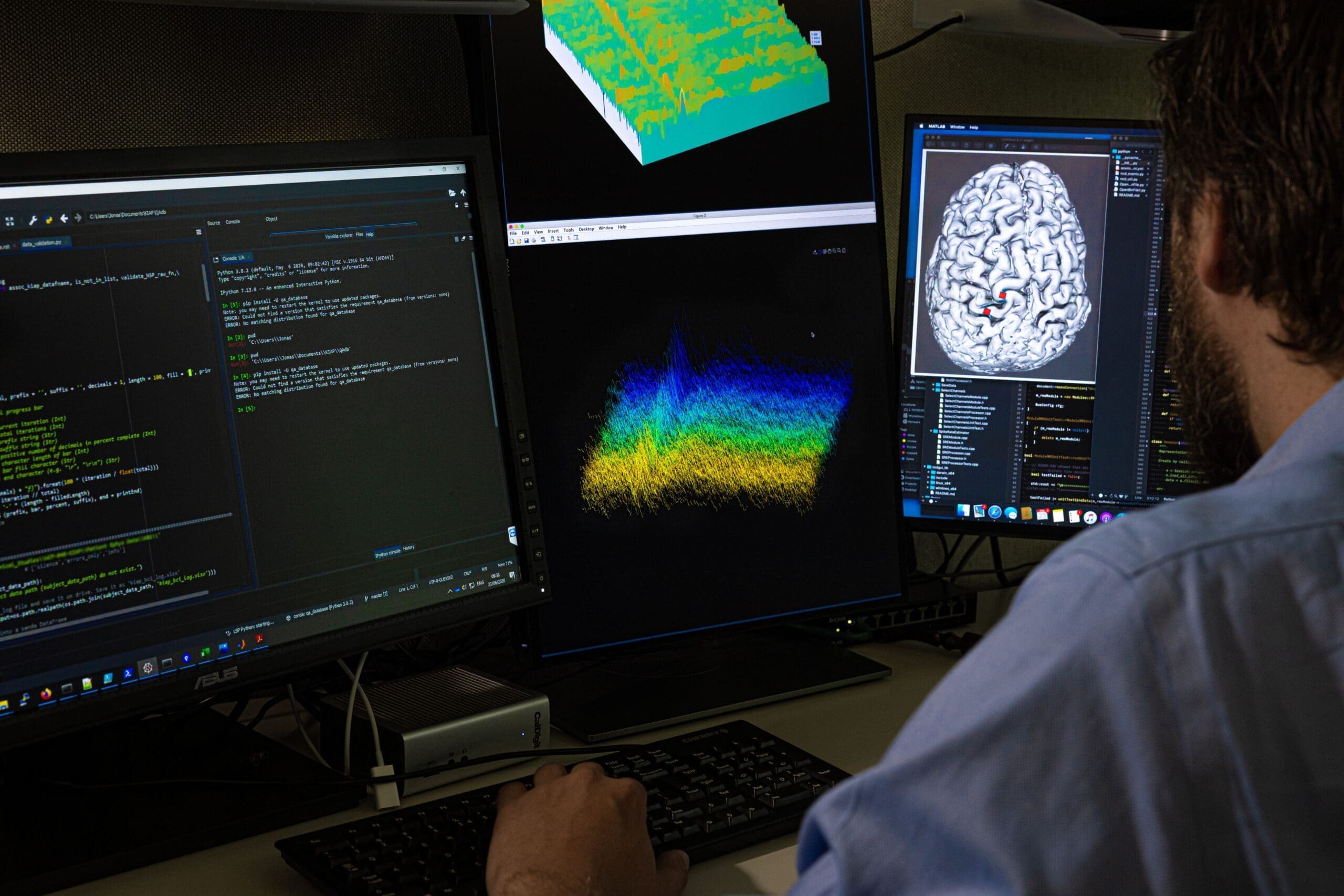
Research and development within the multiple neuro modalities at the Wyss Center, including devices, biology and radiology, are increasingly generating larger and more complex datasets.
Our team seeks to extract useful information about the brain in health and disease from these datasets, using statistical models, algorithms and machine learning.
The goal is to uncover trends and patterns towards the development of earlier diagnoses and therapies with higher probability of positive clinical outcomes.
Harnessing multi-modal data for systematic development and discovery
Large, integrated datasets from implantable and wearable monitoring devices, radiological imaging, transcriptomics, brain circuit mapping and other biological approaches, provide an unprecedented opportunity to uncover a wealth of insights and predictive patterns that can impact the fields of diagnostics, healthcare management and therapeutics.
Key focus areas in data analysis and software development
- Design and implement computational tools critical to our understanding of large, brain datasets.
- Develop scientific software tools that fit seamlessly into clinical workflows and patient-specific frameworks.
- Create file harmonizing software to allow processing of a wide range of data types and formats.
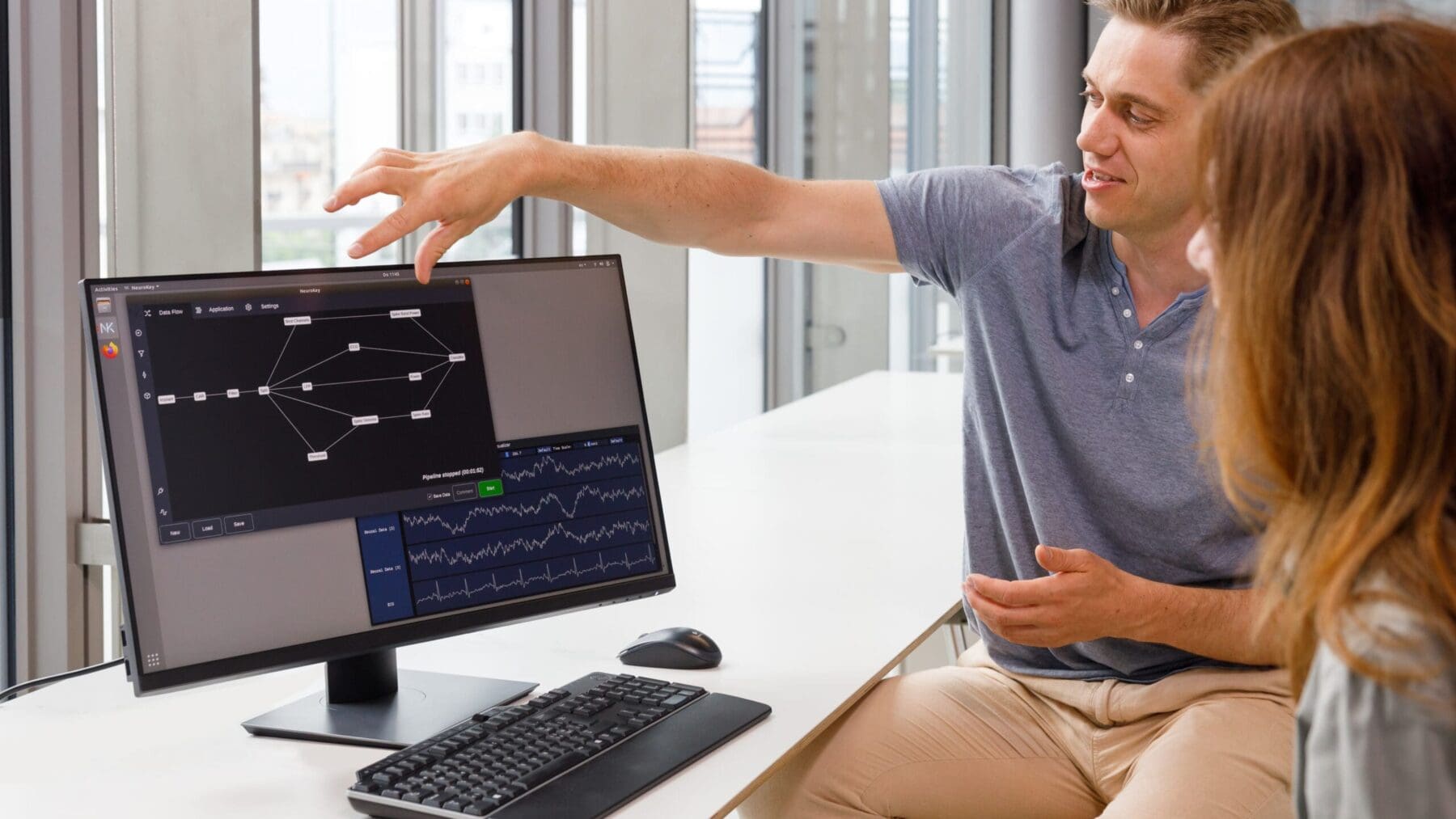
- Build and implement novel algorithms and real-time (or off-line) data processing software for brain-computer interface applications, long term brain monitoring, forecasting and management of acute events.
- Develop computational tools in line with medical regulatory requirements and effective deployment in clinical settings.
- Derive novel insights into complex clinical disorders such as epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.

“An unprecedented quantity, quality and reliability of data is currently being generated by novel neurotechnologies, including the ones we develop at the Wyss Center. This is expected to enable digital biomarker identification and unparalleled insights into disease. Our goal is to use these insights in order to improve diagnostics, therapies and care for patients with neural disorders.”
Artificial intelligence for neural signal decoding
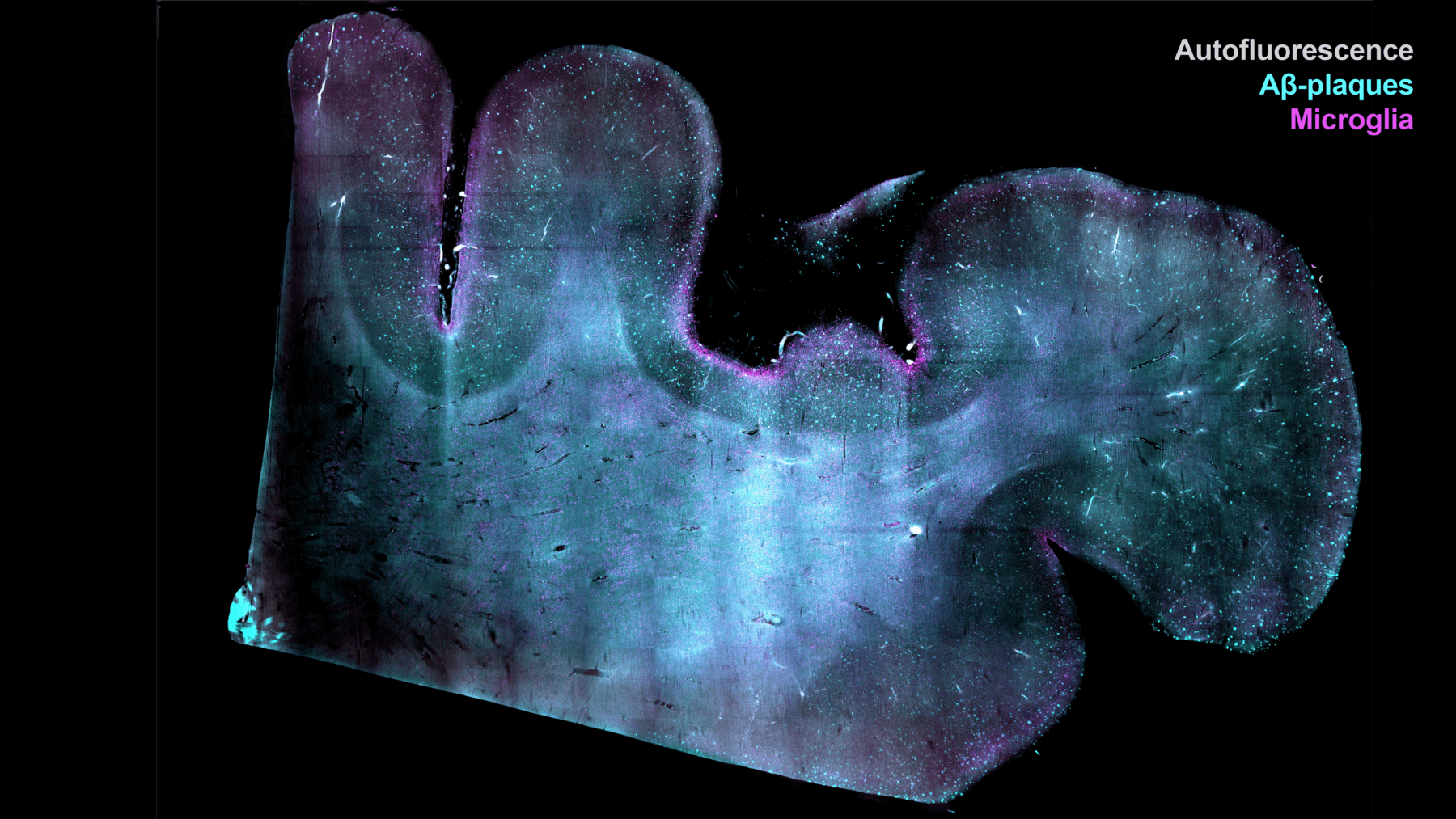
A collaboration between the Wyss Center, University of Geneva/Unit of anatomy, and TU Dresden/Center for Systems Biology Dresden is exploring efficient algorithms for image-based biology with large datasets. The team has focused on new algorithms to reduce the memory footprint and accelerate analysis of very large datasets acquired in our microscopy facility, in real time. Known as pAPRica, the innovative computational imaging pipeline reduces the memory and compute costs of light-sheet microscopy data by about 100x, and it can scale to process PetaByte-sized datasets. Fluorescent image of a large human brain sample acquired using pAPRica. Credit: Wyss Center / Lamy lab – Human Brain Mapping project / TU Dresden / MPI-CBG / CSBD
Team
Updates